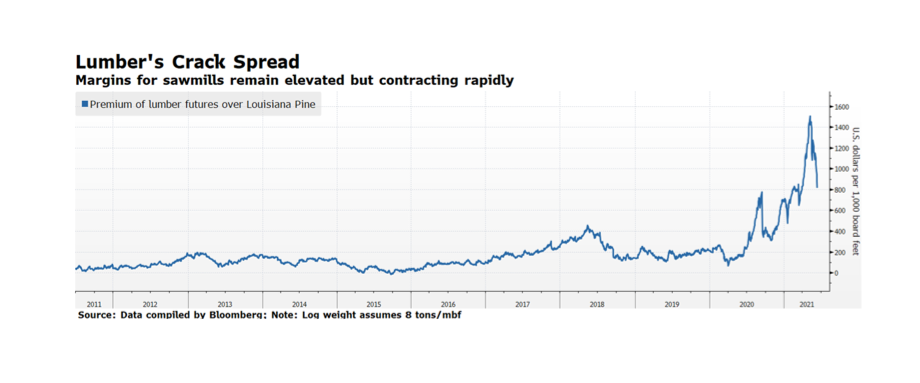
Consumers of lumber products may finally see an end to soaring prices. Lumber crack spreads (the difference in prices of finished lumber and raw timber) have been rapidly falling since peaking in early May. Specifically, the measure on this week’s chart uses the CME futures spot rate of random length softwood 2x4s used in construction minus the Timber Mart-South US Louisiana Pine Sawtimber spot rate. Both indices are falling with finished board prices falling at a faster pace.
There are a variety of reasons why finished lumber prices surged, ranging from a beetle infestation in western Canada and the US Pacific Northwest, strong pandemic-stimulated single family housing demand, glue shortages related to the storm-induced petrochemical plant shutdowns in Texas earlier in the year, and a lack of truckers and workers for sawmills. This confluence of events may be playing out in other industries and be part of why the Fed considers rising key consumer and producer prices transitory and not permanent. Nonetheless, inflationary concerns that recently unnerved the capital markets will likely continue to arise for some time to come. [chart courtesy Bloomberg LP © 2021]