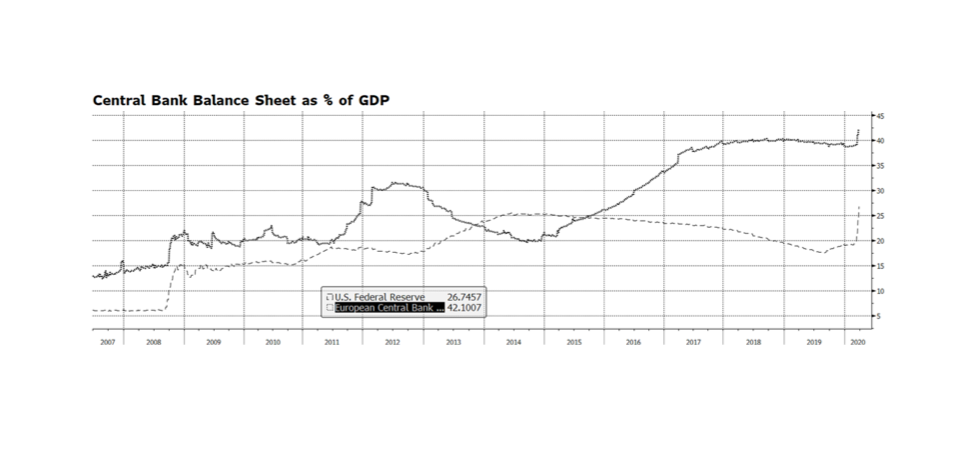
The US Federal Reserve has taken several powerful steps in recent weeks ranging from lowering policy interest rates, intervening in credit markets to provide stability and re-engaging in asset purchases, also known as QE. The amount of monetary stimulus is unprecedented and staggering. Since March 4, the Fed’s balance sheet has expanded nearly $1.6 trillion through their asset purchase plan, accumulating Mortgage Backed Securities, Treasuries and Corporate Credit. That is an incredible amount of expansion in such a short period of time considering that it took some 15 months during the financial crisis from when the QE program began to reach an equivalent level of assets. Some are concerned that the Fed has expended all of its monetary tools and that is a real concern given policy rates are at or near zero. The balance sheet now stands near $5.9 trillion, a level that just a few years ago would have seemed unimaginable. But it could become even larger. The Fed’s balance sheet represents nearly 27% of US GDP. By contrast the European Central Bank’s balance sheet stands at over 42% of European Union GDP. The Bank of Japan stands at over 100% of GDP. The Fed’s asset purchase program could even become more active and remain manageable, especially considering the relative vibrancy of our economy compared to Europe and Japan. [chart courtesy Bloomberg LP © 2020]
© 2024 Wilde Capital Management
Theme by Anders Noren — Up ↑