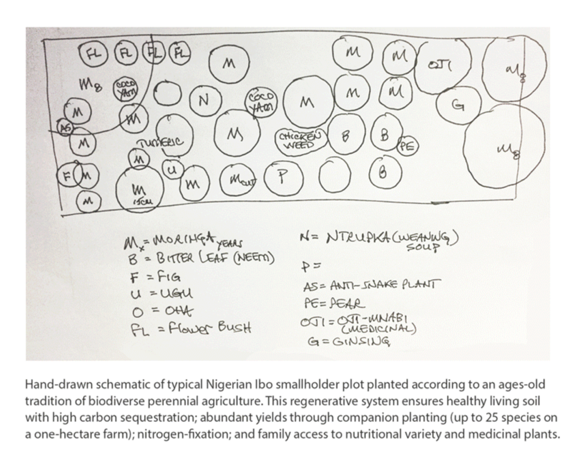
On November 6th, we got a clever hashtag mention — #climateshot – and a “Global Action Agenda”: Increase investment in agricultural research and innovation to create more climate-resilient, low-emission technologies and practices; Focus at least a third of agricultural research and innovation investments deliver demand-driven solutions across food systems, to protect nature and limit climate change; Showcase successful business models and promote public-private partnerships that deploy these innovations on the scale needed to meet the climate and food security challenge; Forge consensus on the evidence of what works, and facilitate inclusive dialogue among food and climate champions around the world. A lot of the right stakeholders (160 institutions, NGOs, countries and companies) are at the table, and there are four key initiatives: “The 100 Million Farmers Multi-Stakeholder Platform, led by the World Economic Forum. The Global Research Alliance on Agricultural Greenhouse Gases (GRA) initiative, which brings countries together to find ways to grow more food without growing greenhouse gas emissions. The new CGIAR organisational structure, research and innovation strategy and portfolio of initiatives. ClimateShot allies from the impact investment community comprise over 20 investors, funders and initiatives, including innovative funds aiming to mobilise over US$5 billion in financing to transform agriculture for people, nature and the climate.” And that is where it all falls down. 20 investors, funders and initiatives and $5 billion in capital is not going to transform anything. (Re)Learning from our world indigenous communities how to shift, or shift back, to regenerative agricultural practices has the potential to address a major carbon problem while also making significant strides in stewardship of water systems, all the while feeding the planet and providing economic opportunity to individuals, families, communities, companies and countries. It starts at the grassroots. This graphic, courtesy of Marc Barasch and Green World Ventures, is a hand illustration of a regenerative approach to smallholder farming already employed in Nigeria which at scale addresses a myriad of economic, nutritional and climatological challenges. What is old is very much new again, and requires activation of those 100 million farmers as well as activation of sufficient capital, from far more than 20 stakeholders, to catalyze a global change.