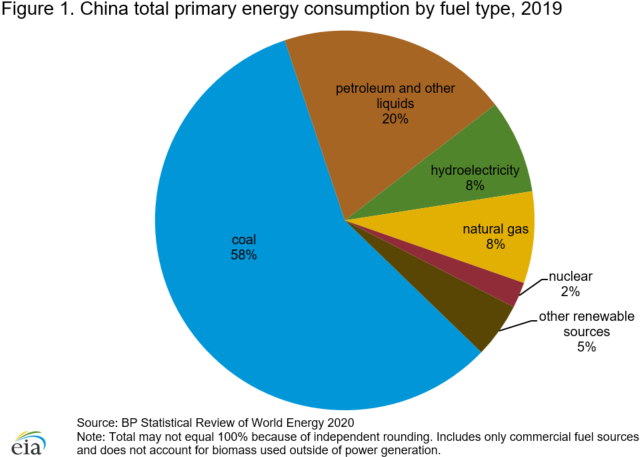
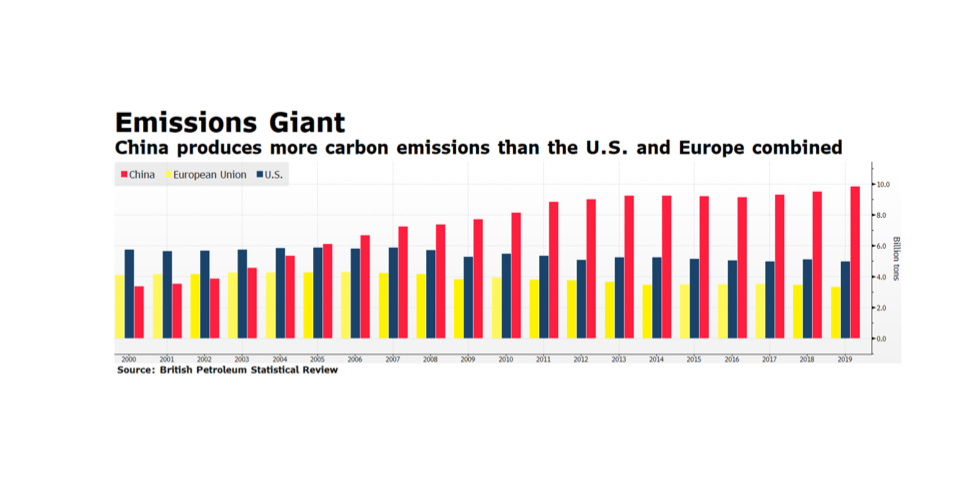
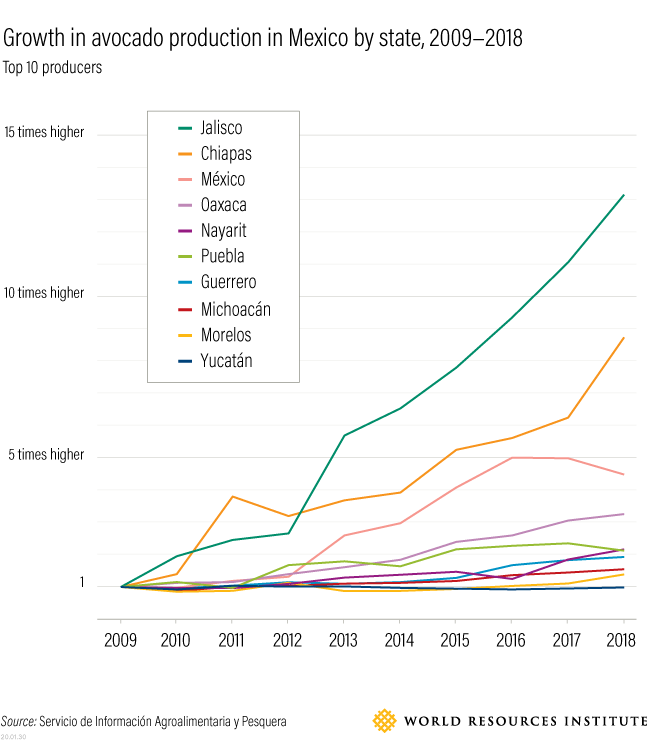
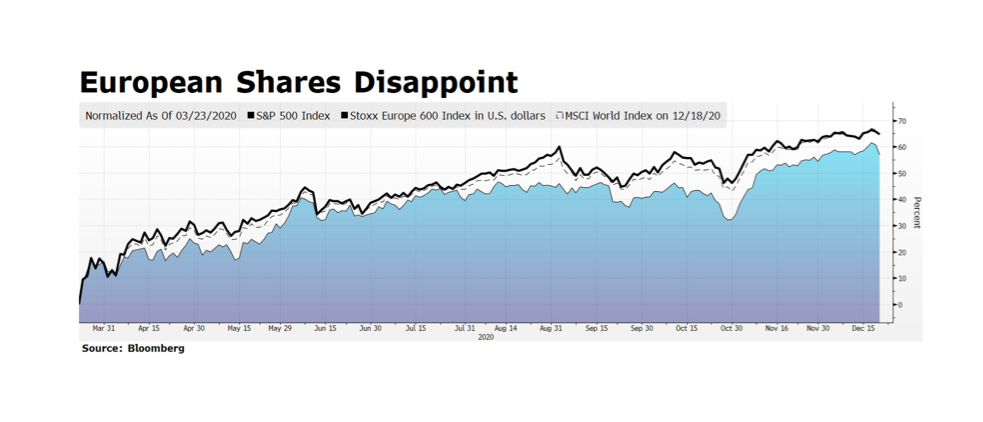
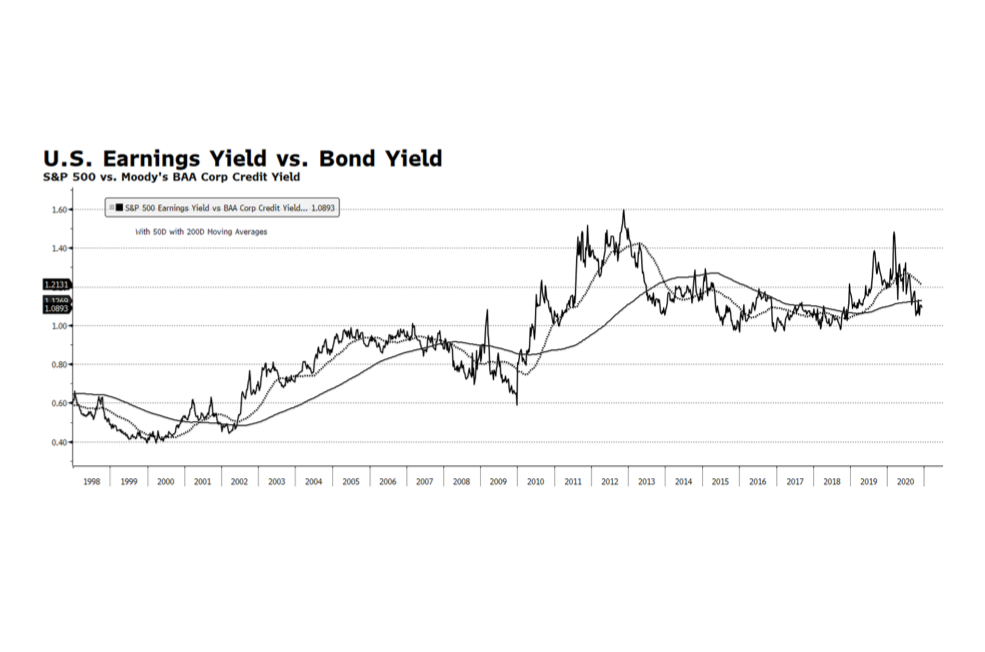
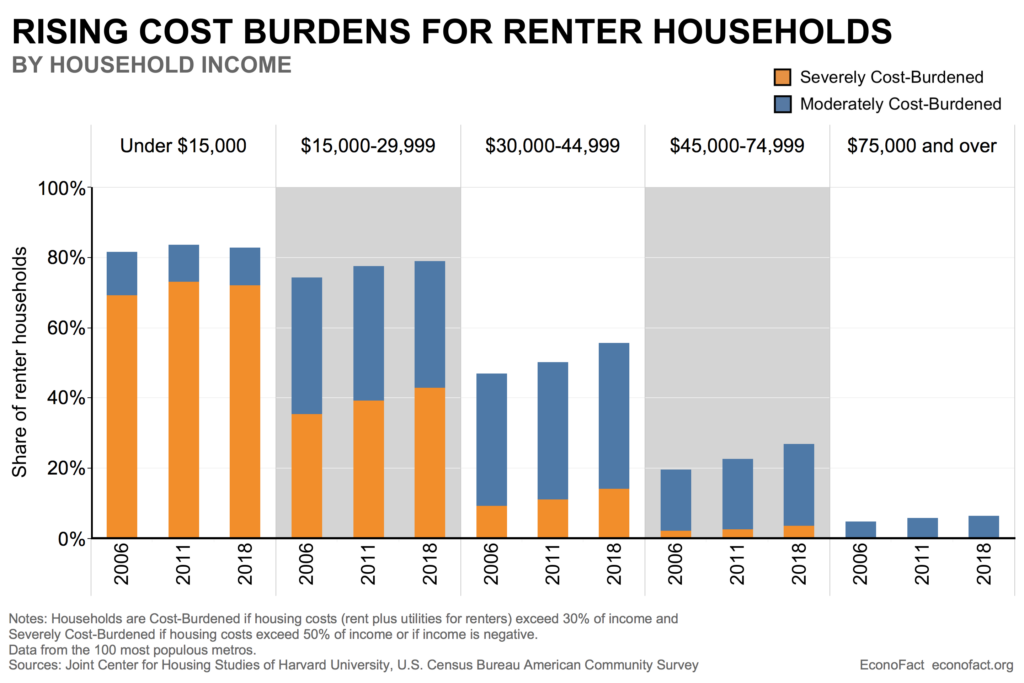
What does a pledge from China of carbon neutrality by the year 2060 actually mean, and how do we measure progress? There are various global targets for climate change mitigation that attempt to quantify what needs to be done so that the global system does not exceed the point of no return, generally seen as a rise of 1.5 – 2.0 degrees Celsius. Under the Paris climate accord, a number of nations committed to carbon neutrality in the next 30 years. China said 40, but as the largest economy on Earth how do we measure their progress? This week’s chart from the US Energy Information Administration country analysis of China (Sept. 2020) is just one hint at the structural challenges China faces in achieving the target. On a per-capita basis China’s carbon footprint is still smaller than the developed West, but their total footprint is more than a quarter of the world’s total output, and their energy mix is just 15% non-carbon and more than half coal. After the pandemic interruption that marked the period around the Lunar New Year, China’s carbon output returned to or even exceeded pre-pandemic levels. We are looking for the steps China will take now to level out carbon growth so that it can begin reversing the trend after 2030, and wonder, even worry whether another 10 years of increasing output takes us past the global point of no return.